Multi-Engine Rating (MER)
2-4 weeks
$5,000 - $10,000
Approximately
Instrument Rating (IR)
1-3 months
$8,000 - $15,000
Approximately
ATPL Exams
4-6 months
Fast-track your aviation journey with expert training, flexible study options, and cost-effective learning plans.
Becoming a pilot is a dream for many, but understanding the process is key to achieving your aviation goals efficiently and effectively.

Comprehensive understanding of costs and financial planning options.

Flexible scheduling options to fit your lifestyle and learning pace.

Guidance on choosing between modular and integrated training options.
CPL is just one milestone in a structured journey to professional flying.
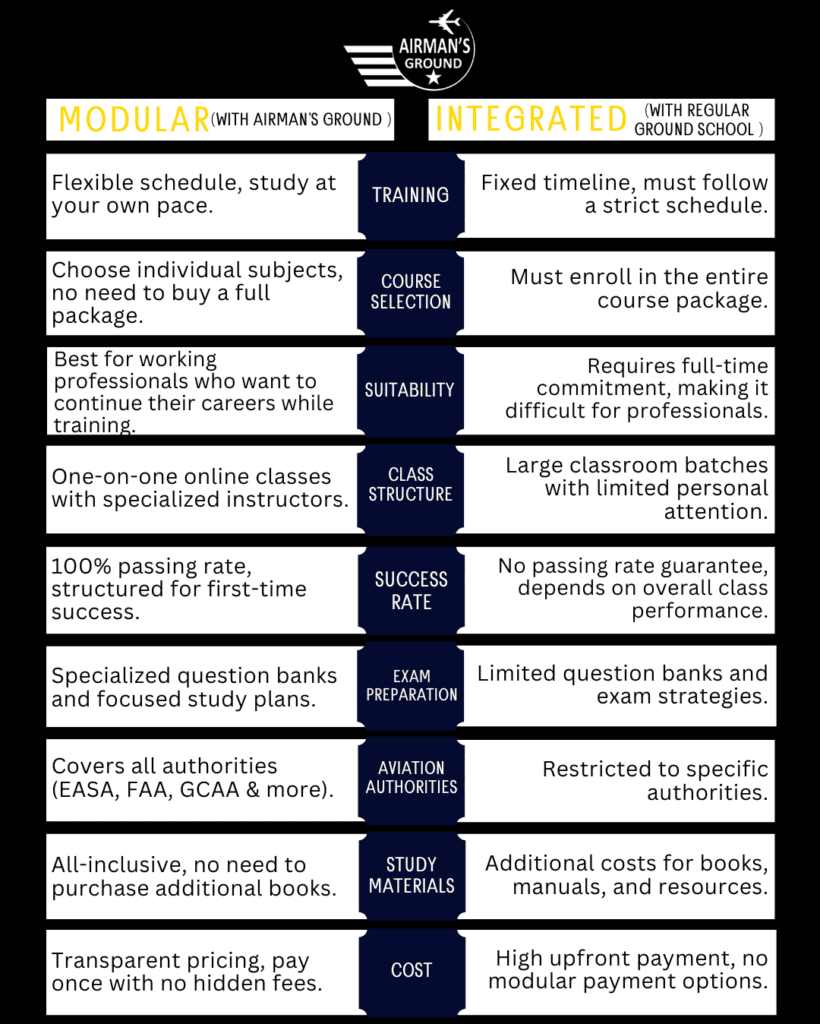
By choosing:
you can fast-track your way to the cockpit without unnecessary expenses.
This is where Airman’s Ground makes a difference! If you complete your ground school preparation with Airman’s Ground, you can save thousands of dollars on training while ensuring first-time exam success with our 100% passing rate.


If you want to fly for personal enjoyment, a Private Pilot License (PPL) is all you need.
With a PPL, you can:
Complete your PPL ground school at home with Airman’s Ground in just 4 months.
For those aiming for an airline career, the journey is more structured and involves multiple steps.
The two main types of professional pilot training are:
Flexible, cost-effective approach that leads to the same professional license.
Faster but more expensive full-time training program.
-
Train at your own pace while managing costs.
Pay as you go, rather than a huge upfront investment.
Identical qualifications with added real-world experience

2-4 weeks

1-3 months

4-6 months
12-24 months
2-3 months
At Airman’s Ground, we guide you through every stage of your pilot journey with structured training, expert coaching, and cost-effective learning plans.


Study, Train & Fly Anywhere – Airman’s Ground prepares students for any aviation authority worldwide:


Here is the summary for your complete airline journey.
From zero to cockpit: your elite pathway to the airline industry, defined.